- HOME
- Information
- Introduction to High-Sensitivity Analysis Techniques for Elemental Impurities ~ Providing solutions for ICH Q3D
Introduction to High-Sensitivity Analysis Techniques for Elemental Impurities
~ Providing
solutions for ICH Q3D
ICH Q3D (Guideline for Elemental Impurities for Drugs) was included in the seventeenth amendment of the
JP. In addition, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare notification *2 indicated that the control
regulations for elemental impurities are scheduled to be included in the eighteenth amendment of the
JP.
In the future, we will be required to deal with elemental impurities not only in new drugs
(formulations and APIs) but also in existing pharmaceuticals, generic pharmaceuticals, general
pharmaceuticals, and additives. Shionogi Pharma Co., Ltd. (Shionogi Pharma Co., Ltd.) has started
outsourced studies corresponding to ICH Q3D and is able to provide solutions.
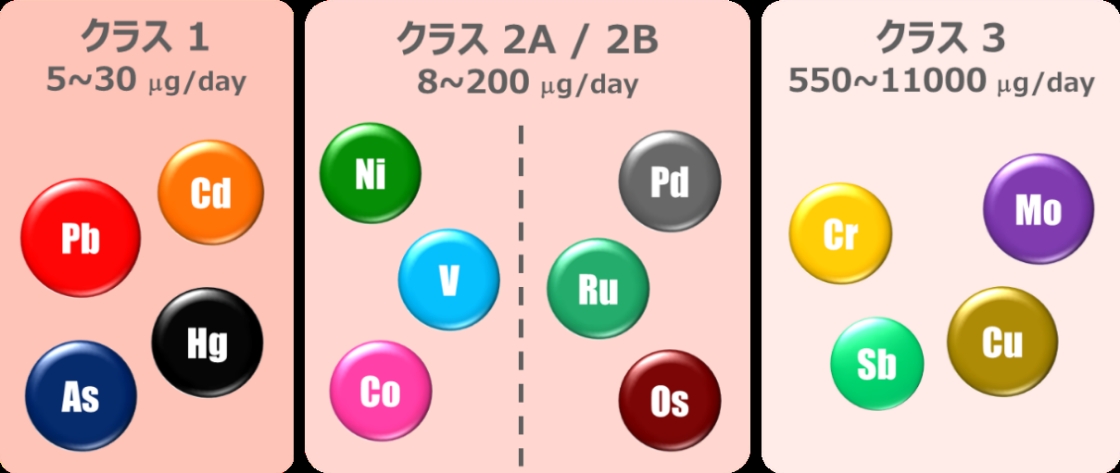
In ICH Q3D, the acceptable daily exposures are determined for each element and route of
administration, as shown below. The conventional arsenic test method and the heavy metal test method had
both sensitivity and specificity. However, these problems were solved by quantitative analysis using ICP
emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) and ICP mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), which are highly sensitive and highly
specific for each element.
Control levels of elemental impurities by ICH Q3D and an example of acceptable daily exposures (PDEs) (oral dosage forms)
Routes of elemental impurity contamination
The following are possible routes of elemental impurities. Even in processes that do not use metal catalysts, the possibility of contamination cannot be denied. Risk assessment is conducted, and the elements considered to be at risk need to be evaluated.
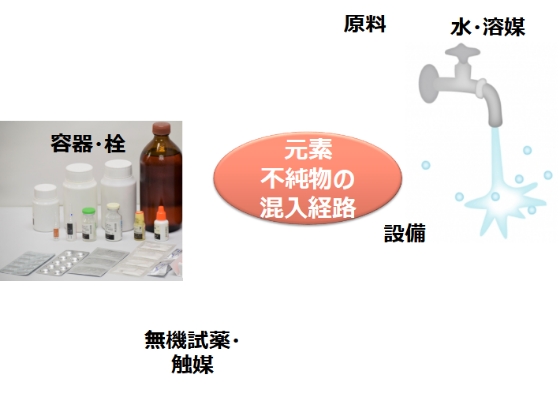
① APIs, excipients and raw materials
・ From catalysts and inorganic reagents intentionally added in the manufacturing process
・ Contamination as impurities in raw materials
・ Mixing from manufacturing facilities and equipment
・ Mixing from water and solvents used in manufacturing processes
・ Vessel/closure system (direct container/plug) to contaminate (elution)
② Drug product
・ Contamination as an impurity of the drug substance or excipient
・ Mixing from manufacturing facilities and equipment
・ Mixing from water and solvents used in manufacturing processes
・ Vessel/closure system (direct container/plug) to contaminate (elution)
Sample preparation
Usually, it is difficult to handle antibiotics such as cephems, for which cross-contamination is a concern in analytical laboratories attached to manufacturing sites. However, Shionogi Pharma can handle a wide variety of samples, ranging from general drugs to highly pharmacologically active substances, including antibiotics, and can be measured. Utilizing pharmaceutical companies' experience as analytical laboratories and using microwave decomposition techniques, it is possible to provide solutions that optimize sample preparation methods to match diverse sample matrices and the elements and compounds of interest without limiting the dosage forms to be measured.
Sample sampling → pretreatment (decomposition by microwave) → ICP-MS
[CEM Japan: MARS6].
Analysis
In Shionogi Pharma, the elemental impurity test method can be established using ICP-AES and ICP-MS (e.g., setting of test method, analytical method validation, actual measurement). Sensitive quantitative analysis (limit of quantification of less than 1/10 of the acceptable concentration) is used to meet the requirements of ICH Q3D. Analytical laboratories have been inspected by foreign authorities and provide reliable data that can be adapted to Data Integrity applications abroad.


ICP-AES ICP-MS
[Shimadzu: ICPE-9000] [Thermo Fisher Scientific: iCAP RQ]
Assessment Case
Shionogi Pharma can provide solutions for elemental impurity assessment in response to developmental stages (early developmental to commercial) such as the following cases. Ask you to make suggestions in accordance with your request, not only for setting test methods but also for designing management strategies.
<Case of Early Development ①>
All 20 elements assessing risk were picked up by referring to ICH Q3D class 1/class 3 and EP9 0 < 5.20>
Metal catalyst or metal reagent residues in early drug substances (poorly soluble). Sample preparation
was performed by a microwave decomposition device, and elemental screening by simultaneous analysis
was performed using ICP-MS.
<Case of Commercial Products ②>
Analytical method validation was performed by setting up a test method for elemental impurity
determination (microwave decomposition equipment + ICM-MS) for oral solid drug product A containing
poorly soluble excipients. Some of the validation results (examples of class 1 elemental impurities) are
shown in the table below.
Analytical method validation results for elemental impurities (class 1) in tabular oral solid dosage form A.
| Cd | Pb | As | Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stipulate in ICH Q3D Option 1 Acceptable concentration (μg/g) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3 |
| Quantification limit (μg/g) of the test method set. | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.15 | <0.3 |
| Linearity (5 concentrations). | 0.99998 | 0.99997 | 0.99994 | 0.99997 |
| Trueness (recovery %) n=3 | 92.5~98.4 | 100.5~102.2 | 97.3~101.4 | 98.7~100.9 |
| Repeatability(RSD %) n=3 | 3.2 | 0.97 | 2.4 | 1.1 |
Shionogi Pharma started its business on April 1, 2019 with the mission of becoming a technology-development mono-building company (CDMO) trusted by its clients. In addition to developing manufacturing methods for APIs and developing drug formulations for commercial production, we have a system that allows one-stop provision of full-range services, including analytical method development and equipment design support through pharmaceutical engineering technologies.
In addition to elemental impurities, Shionogi Pharma accepts the establishment of analytical methods and control strategies for various impurities, including nitrosamines and other hazardous substances, residual solvents (ICH-Q3C), and mutagenicity impurities (ICH-M7). Please feel free to consult with us.
* 1 ICH Q3D (Guidelines for Elemental Impurities in Drugs)
https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000235612.pdf
*2 Refer to Section 8 (2) of Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare notification (No. 628 No. 1 of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare on June 28, 2019)
https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000230314.pdf
* 3 CDMO:Contract Development Manufacturing Organization
Topics
- 2022/09/09
- TopicsIntroduction to High-Sensitivity Analysis Techniques for Elemental Impurities ~ Providing solutions for ICH Q3D
- Introduction to High-Sensitivity Analysis Techniques for Elemental Impurities ~ Providing solutions for ICH Q3D
- 2022/09/09
- TopicsA novel freeze-drying method using controlled freeze-drying technology
- A novel freeze-drying method using controlled freeze-drying technology
- 2022/09/09
- TopicsAnti-cancer Drugs Exposure Evaluation Services
- Anti-cancer Drugs Exposure Evaluation Services
- 2022/09/09
- TopicsManufacturing facilities for highly potent APIs
- Manufacturing facilities for highly potent APIs
- 2022/09/09
- TopicsIntroduction to Technologies for Continuous Manufacturing of Drug Proucts
- Introduction to High-Sensitivity Analysis Techniques for Elemental Impurities ~ Providing solutions for ICH Q3D
